

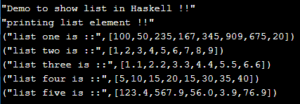
The : operator appends an item to the beginning of a list. Lists are used to hold multiple values of the same type. You can return () from an I/O action if you don't want to return anything.īasic data types can be easily combined in two ways: lists, which go in, and tuples, which go in (parentheses). You can think of this as similar to the void keyword in C family languages.
The final type worth mentioning here is (), pronounced "unit." It only has one value, also written as () and pronounced "unit." The first two are instances of Integral, and the last three are instances of Fractional.

There are five numeric types in the Haskell "prelude" (the part of the library you get without having to import anything):
#Haskell tutorial code
The second is an interpreter that lets you write Haskell code and get feedback right away. The first compiles Haskell libraries or applications to binary code. Once you've installed GHC, you get two programs you're interested in right now: ghc, and ghci. GHC binaries are available for GNU/Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, Windows, and Solaris. Its closest popular relative is probably the ML family of languages (which are not, however, lazy languages). Haskell is a functional (that is, everything is done with function calls), statically, implicitly typed ( types are checked by the compiler, but you don't have to declare them), lazy (nothing is done until it needs to be) language. 9 Topics that don't fit in 10 minute limit.A Gentle Introduction to Haskell (English, File:GentleFR.There are many good Haskell tutorials and books.
#Haskell tutorial install
If you encounter a Could not find module ‘Control.Parallel’ error, please install the parallel library with cabal install -lib parallel Where to go from here
A +RTS -N2 2.14s user 0.02s system 149% cpu 1.449 totalĬongratulations! You are now programming your multicore! Note that in versions of GHC prior to GHC 7, you can leave off the -rtsopts flagĪnd now we can run our multicore program. Import Control.Parallel main = a ` par ` b ` par ` c ` pseq ` print ( a + b + c ) where a = ack 3 10 b = fac 42 c = fib 34 fac 0 = 1 fac n = n * fac ( n - 1 ) ack 0 n = n + 1 ack m 0 = ack ( m - 1 ) 1 ack m n = ack ( m - 1 ) ( ack m ( n - 1 )) fib 0 = 0 fib 1 = 1 fib n = fib ( n - 1 ) + fib ( n - 2 )Ĭompiling with -threaded and optimizations on: Probably was "Hello, world!", so let's do that: If you've learned to program another language, your first program done.Īnd you are presented with a prompt. Alternatively, if you are on Windows, you may choose WinGHCi in the Start menu. If you have installed the Haskell Platform, open a terminal and type ghci (the name of the executable of the GHC interpreter) at the command prompt. Try Haskell provides a less complete but quicker way to give Haskell a shot.
#Haskell tutorial free
If you encounter difficulty, feel free to reach out to the Haskell community. The installation should be supported on most operating systems. The Platform comes with GHC, the de-facto standard Haskell compiler, and other tools that will help you program Haskell. The recommended way to get started with programming Haskell is the Haskell Platform. 4.1 Write your first parallel Haskell program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
